g2o库使用
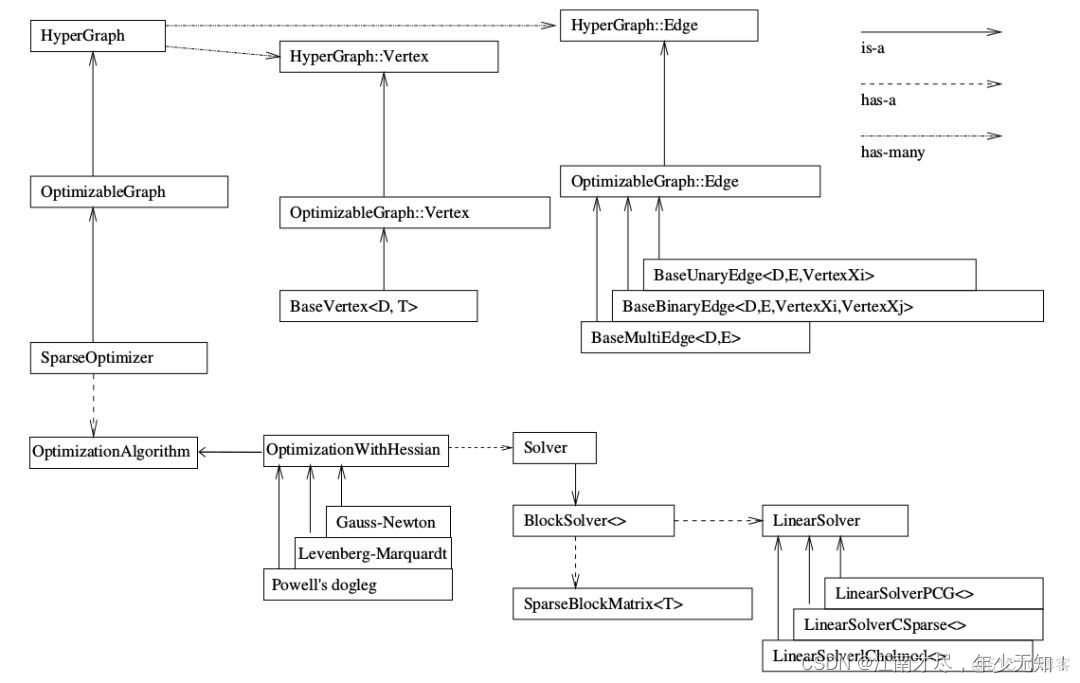
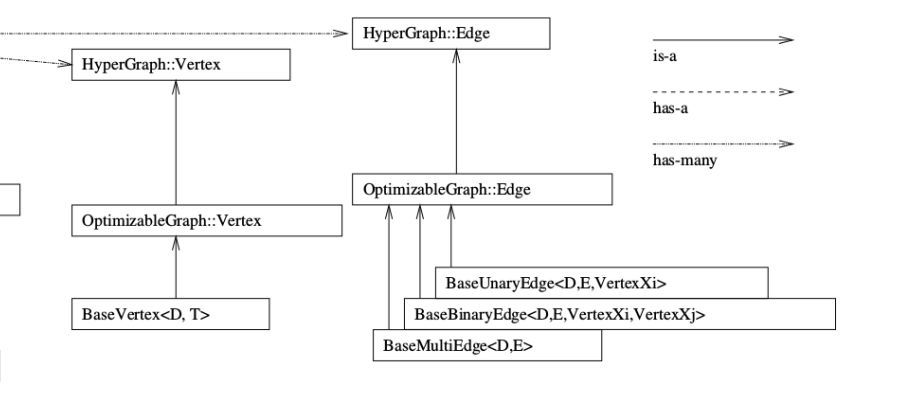
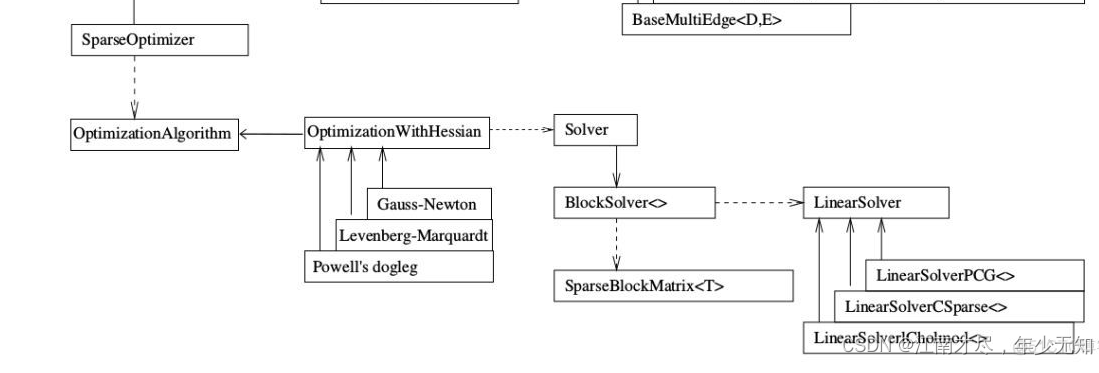
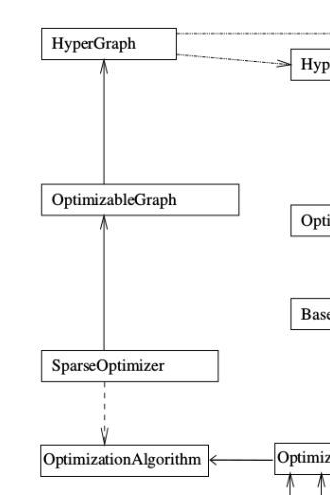
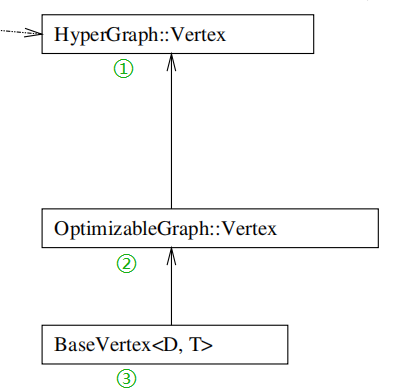
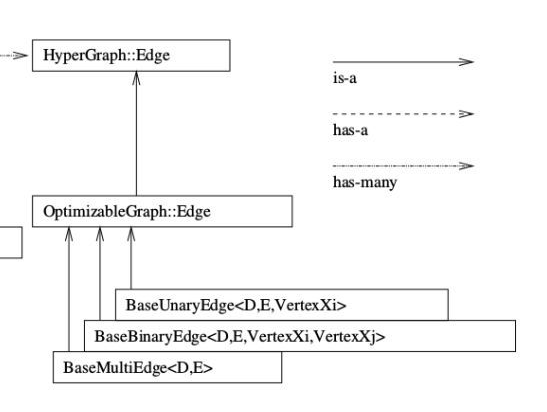
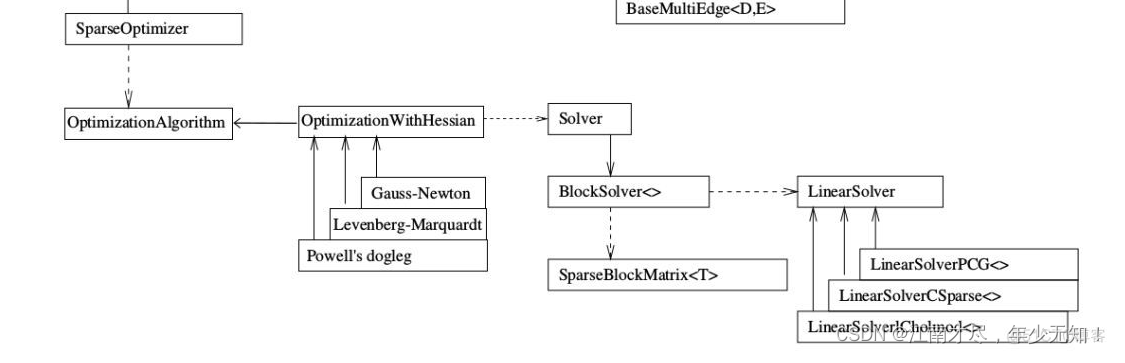
上面是g2o库的框架,非常的清晰。学习g2o库一定要先看这个框架图,而且一定要注意箭头的不同类型,有的是is-a也就是继承类型,有的是has-a和has-many是包含类型。
g2o库的使用过程一般包含以下步骤:
1.顶点和边类型定义(也就是继承父类,重写自己的顶点和边)
2.构建图优化实例,配置求解器,指的是下面的部分:
3.添加顶点和边,构建求解图
4.执行优化
顶点定义
g2o库本身有一些库的定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 VertexSE2 : public BaseVertex<3 , SE2> VertexSE3 : public BaseVertex<6 , Isometry3> VertexPointXY : public BaseVertex<2 , Vector2> VertexPointXYZ : public BaseVertex<3 , Vector3> VertexSBAPointXYZ : public BaseVertex<3 , Vector3> VertexSE3Expmap : public BaseVertex<6 , SE3Quat> VertexCam : public BaseVertex<6 , SBACam> VertexSim3Expmap : public BaseVertex<7 , Sim3>
D指的是Dimension就是要优化变量的维度,T是EstimateType指的是变量的类型。
一般重写边需要考虑一下函数就行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 virtual bool read (std::istream& is) virtual bool write (std::ostream& os) const IO操作一般不需要重写,声明一下就行 virtual void oplusImpl (const number_t * update) · 顶点更新函数,就是待优化变量的更新操作,根据边求出增量之后,用这个函数对变量进行更新 virtual void setToOriginImpl () 顶点重置函数,顶点被重置为优化变量的原始值
实例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class CurveFittingVertex : public g2o::BaseVertex<3 , Eigen::Vector3d>{ public : EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW virtual void setToOriginImpl () { _estimate << 0 ,0 ,0 ; } virtual void oplusImpl ( const double * update ) { _estimate += Eigen::Vector3d (update); } virtual bool read ( istream& in ) virtual bool write ( ostream& out ) const };
边的定义
BaseUnaryEdge是一元边,BaseBinaryEdge是二元边,BaseMultiEdge是多元边。
1 2 BaseBinaryEdge<2 , Vector2D, VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap> 其中2 是指这个测量值是二维的,Vector2D是测量值,VertexSBAPointXYZ是边连接的一个顶点,在SLAM中一般指路标,VertexSE3Expmap是另一个顶点,一般指位姿顶点。
同样的,继承边需要重写以下函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 virtual bool read (std::istream& is) virtual bool write (std::ostream& os) const IO函数一般不做重写 virtual void computeError () 根据顶点和重投影公式计算和观测值之间的误差。 virtual void linearizeOplus () 计算当前节点值下该误差对优化变量的偏导数,也就是Jacobian
另外,边也有一些函数指的注意(顶点同,但是没有列出来)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 _measurement:存储观测值 _error:存储computeError () 函数计算的误差 _vertices[]:存储顶点信息,比如二元边的话,_vertices[] 的大小为2 ,存储顺序和调用setVertex (int , vertex) 是设定的int 有关(0 或1 ) setId (int ):来定义边的编号(决定了在H矩阵中的位置)setMeasurement (type) 函数来定义观测值setVertex (int , vertex) 来定义顶点setInformation () 来定义协方差矩阵的逆
边定义的示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class CurveFittingEdge : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1 ,double ,CurveFittingVertex>{ public : EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW CurveFittingEdge ( double x ) : BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) { } virtual void computeError () override const CurveFittingVertex *v = static_cast <const CurveFittingVertex *> (_vertices[0 ]); const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate (); _error(0 , 0 ) = _measurement - std::exp (abc (0 , 0 ) * _x * _x + abc (1 , 0 ) * _x + abc (2 , 0 )); } virtual void linearizeOplus () override const CurveFittingVertex *v = static_cast <const CurveFittingVertex *> (_vertices[0 ]); const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate (); double y = exp (abc[0 ] * _x * _x + abc[1 ] * _x + abc[2 ]); _jacobianOplusXi[0 ] = -_x * _x * y; _jacobianOplusXi[1 ] = -_x * y; _jacobianOplusXi[2 ] = -y; } virtual bool read ( istream& in ) virtual bool write ( ostream& out ) const public : double _x; };
添加边和顶点,构造优化图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<3 , 1 >> BlockSolverType; typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton (g2o::make_unique <BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique <LinearSolverType>())); g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; optimizer.setAlgorithm (solver); optimizer.setVerbose (true ); CurveFittingVertex *v = new CurveFittingVertex (); v->setEstimate (Eigen::Vector3d (aest, best, cest)); v->setId (0 ); optimizer.addVertex (v); for (int i = 0 ; i < PointNum; i++) { CurveFittingEdge *edge = new CurveFittingEdge (x_data[i]); edge->setId (i); edge->setVertex (0 , v); edge->setMeasurement (y_data[i]); edge->setInformation (Eigen::Matrix<double , 1 , 1 >::Identity () * 1 / (w_sigma * w_sigma)); optimizer.addEdge (edge); } cout << "start optimization" << endl; chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now (); optimizer.initializeOptimization (); optimizer.optimize (10 ); chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now (); chrono::duration<double > time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double >>(t2 - t1); cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count () << " seconds. " << endl; Eigen::Vector3d abc_estimate = v->estimate (); cout << "estimated model: " << abc_estimate.transpose () << endl;